The boost pressure sensor is also called the MAP sensor. Installed on certain types of vehicles, the turbo pressure sensor allows the ECU to calculate various information about engine intake, such as injection duration.


Are you looking for a car scanner ?
What is the purpose of the boost pressure sensor?
The boost pressure sensor is commonly found on diesel vehicles equipped with a turbocharger.
The role of the MAP sensor (Manifold Absolute Pressure) is to measure the intake air pressure as it enters the engine. It then transmits this information to the engine control unit (ECU), which adjusts the amount of fuel injected accordingly.
About the turbocharger
Since the boost pressure sensor is installed on diesel or petrol vehicles with a turbocharger, it is essential to understand how the turbocharger works.
In 1916, Auguste RATEAU developed a turbocharger model for aircraft engines. This technology was later applied to sports cars in the 1930s. However, it was only in 1962 that the first commercial version of the turbocharger was released.
The turbocharger is installed on internal combustion engines, both petrol and diesel. Its role is to increase engine power by compressing the intake gases, allowing better cylinder filling with air.
The turbocharger can increase engine power and efficiency while also reducing fuel consumption on smaller engines.

The turbocharger consists of a turbine driven by the exhaust gases exiting the engine. This turbine is connected via a shaft to a compressor located in the engine's intake duct.
The compressor draws in and compresses ambient air, sending it into the cylinders. This improves cylinder filling compared to vehicles without a turbocharger, where cylinders are filled by the vacuum created by the piston descending during the intake phase.
How the MAP sensor works
The introduction of the turbocharger required some modifications to the engine, including adding a component to monitor air pressure in the intake: the MAP sensor.
The MAP sensor is made of ceramic containing pressure-sensitive measurement resistors. When the boost pressure sensor detects a pressure increase or decrease, it sends this information to the ECU, which reacts accordingly.
Diagnosing your boost pressure sensor
Symptoms of a faulty MAP sensor
If your boost pressure sensor is faulty, here are some symptoms to watch for:
- Your car's idle speed is irregular
- You notice significant power loss, such as a sudden loss of boost when pressing the accelerator
- Your car accelerates in jerks
- The orange engine warning light on your dashboard is illuminated
Testing your boost pressure sensor
To confirm a fault with the boost pressure sensor, you can use a car diagnostic tool.
First, locate your OBD port. If you're unsure where it is, you can use our app "Where is my OBD2 port? Find it!".
Next, connect your diagnostic tool and perform your scan.
Here is a list of generic fault codes related to boost pressure:
- P0540: Abnormal input voltage detected in the intake heater circuit
- P0234, P0235: Engine overboost condition
- P0236, P0237, P0238: Intake manifold absolute pressure sensor A
- P0239, P0240, P0241, P0242: Intake manifold absolute pressure sensor B
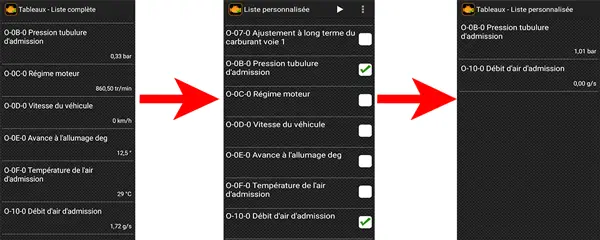
To check the boost pressure sensor using the EOBD Facile software, follow these steps:
Open the EOBD Facile application. You can find it on the Apple Store and Google Play Store. Click on the "measure" tab, then the "table" tab, and finally "full list".
Select the code 0-0B-0 for intake manifold pressure and code 0-10-0 for intake air flow. For example, the intake manifold pressure is 1 bar when the engine is off, and the air flow is 0 g/s.
What causes the failure?
Here are the possible causes of a boost pressure sensor failure:
- A leak in the intake manifold
- A clogged or malfunctioning air filter
- A blocked intake manifold
- A defective sensor
- An issue with the electrical wiring

Are you looking for a car scanner ?
How to replace the boost pressure sensor?
Example on the Renault Grand Scenic 2
Start by disconnecting the negative terminal of the battery.
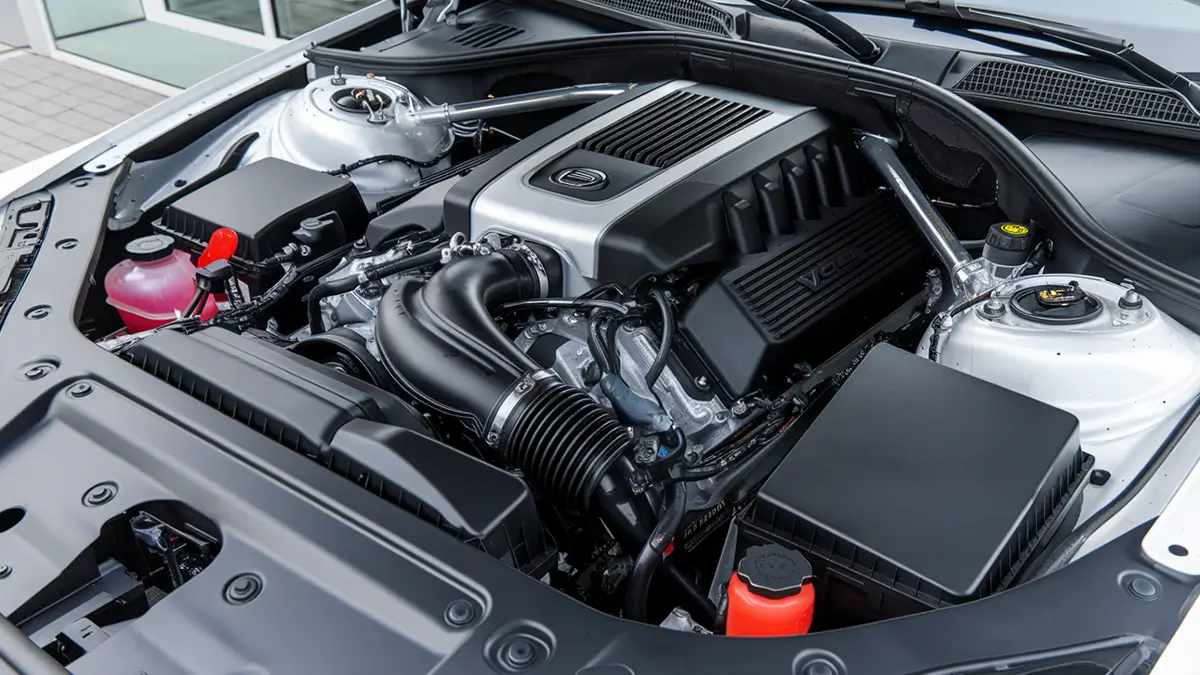
Next, locate the boost pressure sensor. On the Grand Scenic 2, it is located in the middle right of the engine, slightly to the left of the battery when facing the engine.
Once located, unplug its electrical connector (1). Then loosen the fixing nut (2).

Simply pull it out! Make sure to compare the old sensor with the new one to ensure the specifications match.
Finally, connect the new turbo pressure sensor in place, then reattach any components you removed during the process. You can verify everything is working correctly by connecting a Renault diagnostic tool to your Scenic, Clio...