The alternator is essential for the proper functioning of your car and is part of the engine accessories. It supplies electricity to the vehicle. Indeed, cars are increasingly equipped with electronics, requiring a well-charged battery.
So, what is the purpose of the alternator, how does it work, and how can you detect faults?


Are you looking for a car scanner ?
The alternator: its history
Are you familiar with how the alternator works? Its role is to convert the RPM of your engine into electricity for your battery. This process applies regardless of the type of engine.
Let’s go back in time to 1821. At that time, Faraday had the idea of rotating a wire through which an electric current flows under the influence of a magnetic field. This marked the birth of the principle of electricity.
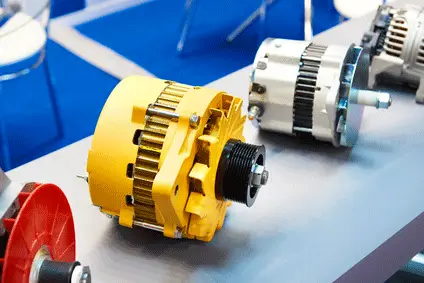
Fast forward to 1960, the end of the dynamo era. The dynamo was beginning to show its limitations, and new models of electric vehicles were emerging on the market. This is when car manufacturers started equipping vehicles with alternators.
In 1961, Chrysler became the first car manufacturer to mass-produce alternators, initially for competition models.
Components of this part
The alternator consists of several parts:
- A generator
- A rectifier
- A regulator: the regulator is only present in the most recent models. It operates using transistors and manages the alternator's operation.
Additionally, these elements are equally essential:
- A fixed coil, also known as the stator
- An electromagnet, called the rotor
- A belt
How does the alternator work and what is its purpose?

The alternator converts the mechanical energy of an engine into electrical energy. It is the electricity source for your car. Thanks to it, you can lower and raise the windows or listen to music in your car. The alternator also powers your headlights. It is also responsible for recharging your battery while your car is running.
The car alternator uses a magnet (the rotor) and a copper coil (the stator). When the engine is on, the rotor rotates inside the coil, driven by the belt. Several steps then occur:

- The rotation of the magnet (rotor) inside the coil (stator) generates an alternating current.
- This current is rectified to recharge the battery with direct current.
- The regulator adjusts the power supplied by the alternator. It electronically shuts off the alternator when the engine is loaded.
Diagnosing an alternator fault
The noise
Normally, the alternator emits a (very faint) sound produced by electromagnetic pulses. At startup, it may produce a whistling sound, indicating a possible defect. This symptom may result from insufficient electrical charge. The noise could also come from a broken belt. Finally, an over-tensioned belt will cause premature wear, increasing the risk of breakage.
There are several types of noise:
- If you hear a dull noise, it is likely a bearing issue.
- If it is a belt noise, the belt may be too tight, too loose, or worn.
Odours
You may notice a burnt rubber smell in the event of an alternator fault. This could be due to the pulley no longer rotating. This smell results from the friction of the belt between the engine and the pulley. This phenomenon heats the belt, eventually causing it to snap.
Warning light: alternator or battery?
The battery warning light on the dashboard can be one of the early signs of an alternator fault. However, you must verify whether it is indeed the alternator or the battery that is faulty. There is a simple way to check. To do this, use a multimeter set to volts.
First, turn off the engine, then:
- Connect the black lead of your multimeter to the negative terminal of your battery, marked with the - symbol.
- Connect the red lead to the positive terminal, marked with the + symbol.
If the voltage is between 12 and 13 volts, your battery is in good working condition.
If you cannot measure your battery's voltage, check out our tutorial explaining how to perform this test.
Now test the alternator. Start the engine and connect the multimeter leads as described above. The alternator's value should be around 14 volts.
Consequences of an alternator fault
A faulty alternator can affect your car's electrical system:
- Its performance will decrease.
- You may notice reduced brightness in your car's headlights.
- The window operation system may become slower.
Maintaining your car alternator
How to replace it?
You can perform this task yourself. However, if you are a beginner, it is safer to consult a professional mechanic.
Several steps are required:
- First, disconnect the negative terminal of your battery (marked with the - symbol) to cut off the electricity supply to your vehicle. Always remove this terminal first.
- Remove any components obstructing access to the alternator.
- Loosen the alternator belt and remove it.
- You can now dismantle the alternator by unscrewing its mounting bolts.
- Remove the alternator by disconnecting the connectors. Be sure to note their positions and colours.
- Install the new alternator and replace the belt. Adjust the belt tension according to the manufacturer's recommendations.
- Finally, reconnect the connectors and the battery.
What is the cost of an alternator?
This part can be quite expensive, so it is essential to accurately diagnose the cause of the fault before making a decision. Prices range from €100 to €600 for a new alternator. If you hire a professional, labour costs will be added.
Reconditioned parts are available, allowing you to replace your alternator at a lower cost.
The alternator plays a central role in your car's proper functioning, especially in maintaining your battery's maximum power. Whether you have a petrol or diesel engine, an alternator issue can lead to reduced electricity production or even a voltage drop in your battery.
Also, ensure your engine is well-maintained; otherwise, you may notice variations in rotation speed (the engine runs faster or slower). Consequently, the alternator will not be able to charge the battery effectively. In short, do not neglect your engine maintenance—take care of it!

Are you looking for a car scanner ?