Located near the flywheel and crankshaft, the TDC sensor or Top Dead Centre sensor is part of the engine position system and is known to cause various issues related to engine speed and starting.


Are you looking for a car scanner ?
The TDC sensor, also called the crankshaft sensor, is responsible for informing the ECU about the position of the pistons so it can calculate engine speed and adjust fuel injection accordingly.
However, as a four-stroke engine operates (intake, compression, power, and exhaust), a piston positioned at top dead centre can either be in the compression phase or in the exhaust phase depending on the combustion cycle. To determine this information, the ECU relies on the camshaft sensor, which provides this data.

How the TDC sensor works
How does the Top Dead Centre sensor work?
To determine the position of the pistons, the TDC sensor relies on the rotation of the flywheel.
A marker is placed on the toothed wheel to continuously inform the ECU about the position of the pistons: the sensor sends information each time it detects the marker and counts the number of teeth between intervals, allowing the ECU to track the engine's rhythm.
The camshaft sensor then complements this data by specifying the combustion cycle so the ECU can determine in which cylinder and at what moment fuel needs to be injected.
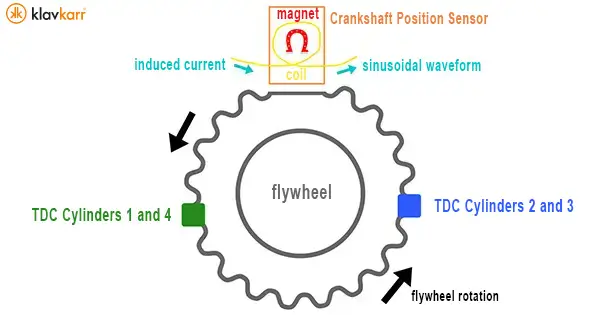
The flywheel is therefore directly linked to the TDC sensor as it measures the information needed by the engine ECU to calculate the engine speed, which corresponds to the rotational speed of the flywheel and crankshaft.
Two types of sensors
Inductive TDC sensors are equipped with a magnet and a coil that enable an electromagnetic reaction: When the teeth pass in front of the metal, they disrupt the magnetic field, generating a current proportional to the flywheel's rotational speed. This electrical signal is then sent to the ECU via two wires in the form of a sine wave voltage.
This system relies on a toothed wheel that generally has two missing teeth as a marker: as soon as the gap between two pulses (= two teeth) is larger, the ECU recognises it as the marker.
However, in modern engines, the crankshaft sensor is active and directly sends an electrical signal to the ECU for every tooth detected. The operating principle is the same but is electronically managed: the passage of a tooth in front of the sensor sufficiently disrupts the current inside, causing a "Hall effect." This system is more expensive but much more precise, especially at low speeds.

Are you looking for a car scanner ?
Testing a faulty TDC sensor
Symptoms of a faulty sensor
A faulty TDC sensor usually results in an inability to start: the ECU does not know the pistons' position and therefore cannot trigger fuel injection and ignition in petrol engines.
However, a vehicle that does not start can also be due to several other issues, ranging from a simple lack of fuel to faulty spark plugs.
If your crankshaft sensor is defective, several symptoms may appear:
- Difficult starting
- An engine that "stutters" and makes noise
- Unexpected stalling
- A non-functioning tachometer
In such cases, the connector may simply be unplugged or damaged, and a small repair may suffice.
Keep an eye on your dashboard as the orange engine warning light may come on, indicating that the limp mode has been activated. This mode is precisely what can cause the symptoms mentioned above.
Performing an automotive diagnostic
As with many other faulty mechanical parts, the resulting symptoms can be difficult to observe and associate with a defective TDC sensor.
An automotive diagnostic can be a very good solution as a fault code will be returned in case of a problem.
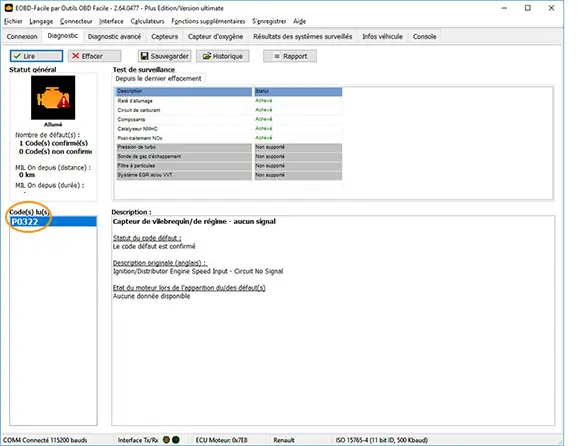
With EOBD Facile, the code P0322 is returned here, which corresponds to a lack of signal. In such cases, be sure to take the time to check the sensor's position, as it may not necessarily be defective but could simply have a connection issue.
We can go further by recording the engine speed during starting to observe whether everything is functioning correctly. This method is useful as it provides information that can be helpful in the absence of a fault code, for example, or as a complement to it.
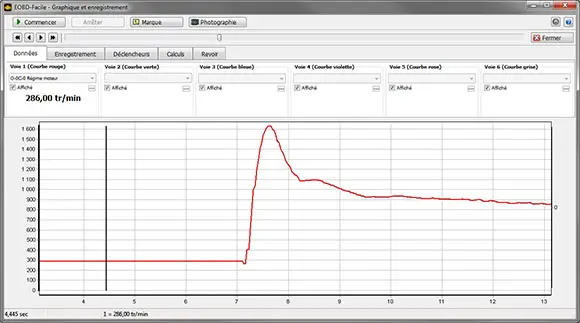
Here, the curve is completely normal, suggesting no starting issues, and the TDC sensor can therefore be ruled out if no fault is returned.
Note that you can also clear your engine warning light if it has come on. Keep in mind that it may light up again if the fault has not been repaired.

Are you looking for a car scanner ?
Checking the signal and resistance
It is also possible to check the electrical signal and resistance using a multimeter and an oscilloscope, depending on the type of sensor:
- For an inductive sensor: You can check the sensor's resistance with a multimeter, which should generally be between 300 and 900 Ω depending on the manufacturer. Also, check the continuity of the wires connecting the sensor to the ECU (0 Ω).
- For a Hall Effect sensor: Here, you will necessarily need an oscilloscope to measure the electrical signal. First, disconnect the connector on the ECU side, then check for a signal by starting the engine.
klavkarr tip: Consider visually inspecting the condition of your TDC sensor. Often, cleaning the connector can be enough to restore a connection. The issue may also come from the air gap, i.e., the space between the sensor and the flywheel teeth, which should be 1mm for optimal detection.