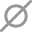
Modern vehicles integrate more and more electronics. To protect these systems, manufacturers have implemented a security gateway, also called “Secure Gateway.” This device restricts certain operations via the OBD port, even when a car diagnostic scanner is used for routine tasks like clearing faults or resetting indicators.
What is it for?
Why is it used and by which brands?
How can I continue to use my car diagnostic scanner?

Are you looking for a car scanner ?

Can't find your light on the list?
Send us an email with information about your car, so we can assist you.

Don't find your car model?
Send us an email with information about your car, so we can assist you.
What is a security gateway?
The security gateway, also known as Secure Gateway, is an electronic protection device installed on many modern vehicles. It acts as a filter between the OBD port (diagnostic socket) and the vehicle’s electronic control units (ECUs).
It prevents certain “sensitive” actions—such as clearing fault codes or resetting dashboard lights—from being executed without prior authentication.
This helps secure the vehicle’s “critical” functions against any unauthorized manipulation.
Which vehicle brands use a security gateway?
In some cases, this secure gateway is built into a dedicated electronic module. In others, the system relies on the manufacturer’s servers to approve or deny access.
Stellantis Group (formerly FCA)
The Security Gateway (SGW) is deployed by Stellantis (formerly FCA) on brands such as Fiat, Jeep, Alfa Romeo, Chrysler, Dodge, and RAM.
By default, this system blocks all active functions via the OBD port (clearing faults, resetting indicators, actuator tests), which then require online authentication through a manufacturer-approved tool.
To restore full access, simply use an SGW bypass module, an adapter placed between the OBD port and the diagnostic scanner that allows you to circumvent these restrictions without going through the official infrastructure.
Renault-Nissan-Mitsubishi Alliance
On Renault, Dacia, and related brands, the security gateway—often called the Renault Secure Gateway by analogy—relies on remote authentication via the manufacturer’s servers.
Sensitive operations (dashboard resets, ECU coding, fault clearing) require the official Renault CLIP tool or third-party software like DDT4All, which can partially bypass the software restrictions.
Unlike Stellantis’s SGW, no plug-and-play bypass module is available for these brands; independent workshops must therefore use either a professionally validated Renault access or advanced software solutions, exercising due caution.

Are you looking for a car scanner ?
Volkswagen Group (VAG)
Volkswagen Group (including VW, Audi, SEAT, and Škoda) integrates a security gateway called SFD (Schutz der Fahrzeugdiagnose).
On recent models, any sensitive operation via the OBD port—clearing faults, coding, or adaptations—requires online authentication with the manufacturer’s servers via the official ODIS tool. Although tightly controlled, it is possible to bypass SFD with an SFD Unlock module, an adapter that emulates manufacturer authorization.
These modules, while unofficial, are widely adopted by independent garages to restore full OBD functions without using the dealer network.
Daimler Group
With Mercedes-Benz, diagnostic security relies on Xentry Lock and the Seed & Key protocol, integrated into the official Xentry Diagnosis platform.
Any sensitive action (coding, adaptation, fault clearing) requires authentication via manufacturer digital certificates and a connection to Daimler’s servers.
To date, no plug-and-play bypass module exists; only official tools or high-end professional scanners with a manufacturer subscription provide full advanced function access.
BMW Group
For BMW and Mini, access to sensitive OBD functions is protected by the E-sys/ISTA platforms and remote certificate-based authentication.
With no plug-and-play bypass available, independent workshops must use modified ENET cables or third-party software to circumvent these locks, which requires technical expertise.
Hyundai-Kia Group
Hyundai and Kia integrate security into the GDS (Global Diagnostic System), their official diagnostic tool for authorized service centers.
This system only blocks advanced functions; most multibrand tools still provide broad access without needing a specific adapter.
Ford
Ford secures its diagnostic functions with IDS/FDRS, requiring remote authentication with official servers to unlock certain operations.
Currently, there is no standardized bypass module, so independent shops must use Ford-approved tools and procedures for advanced functions.
Toyota
Toyota protects certain operations through its Techstream software, which requires validated authentication to access sensitive functions.
Although unofficial tools are emerging, no widely adopted bypass solution exists yet for independent workshops to replace Techstream.
Impact of the security gateway on OBD functions
What you can still do despite the security gateway
Even with this system in place, some operations remain available with a standard diagnostic tool:
- Read fault codes (DTCs)
- Monitor engine data (temperature, voltage, pressure, etc.)
- Access certain sensor information
These actions are considered passive, as they do not alter vehicle operation.
What the gateway blocks without authorization
The restrictions apply to active or safety-critical functions, such as:
- Clearing fault codes after repair
- Resetting indicators (oil change, brake pads, etc.)
- Running actuator tests (injectors, EGR valve, fans…)
- Performing coding or reprogramming
These functions remain inaccessible until the security gateway is unlocked by a compatible method.
Why have manufacturers implemented this automotive gateway?
The goals of this technology are multiple:
- Secure access to sensitive electronic systems
- Protect against cyberattacks or hacking, especially on connected vehicles
- Prevent misuse by non-certified tools
- Ensure compliance with manufacturer procedures
This approach aligns with broader regulations, notably the introduction in 2021 of the ISO/SAE 21434 standard, which defines cybersecurity requirements for connected vehicles. Manufacturers must ensure electronic system protection throughout the vehicle’s lifecycle.
Since 2002, the SAE J2534 “Pass-Thru” standard has required manufacturers to allow certain reprogramming functions for independent repair shops via a standardized tool.
In this context, the security gateway is central to meeting these obligations. However, it also imposes concrete limitations: it restricts electronic interventions performed outside the official network, even for simple maintenance tasks like resetting an indicator or clearing a fault code after repair.
It is therefore recommended that manufacturers comply with this standard.
Solutions to bypass the security gateway
There are several ways to access functions locked by the gateway:
- Use an SGW bypass or adapter
- Employ a manufacturer-approved diagnostic tool
- Create an account on a manufacturer portal
Certain manufacturers offer modules that connect between the vehicle’s OBD port and the diagnostic tool. This device emulates unrestricted access, commonly used in professional settings.
High-end scanners compatible with manufacturer servers allow secure authentication. The tool is recognized by the gateway and permits normally blocked operations.
Several manufacturers grant independent workshops remote access to advanced functions. This paid service usually requires a professional ID.